The Brain
The Astonishing Hypothesis is that You, your joys and your sorrows, your memories and your ambitions, your sense of personal identity and free will, are in fact no more than the behavior of a vast assembly of nerve cells and their associated molecules.
Materialism: brain = mind
Duralism: We possess two sorts of things. We are composed of two sorts of things. We are in part material, but we're also in part spiritual, separate, mental, psychological.
- The creativity and spontaneity of human action
- "I think therefore I am", we don't feel like bodies.
Dualism seems right
- Intelligent begins without bodies
- The survival of the self after the destruction of the body
Dualism is wrong?
- Dualism does not answer important questions
- We now have better understanding of what physical things can do
- Strong evidence for the role of the brain
Neurons
- sensory neurons
- motor neurons
- interneurons
code for intensity:
- number of neurons firing
- frequency of neurons firing
excitatory (agonists) / inhibitory (antagonists)
clusters/networks (computational devices)
- The brain is highly resistant to damage
- The brain is extremely fast
- The brain works through massively parallel processing
sensory information is sent to opposite hemisphere corssing over in pathwasy leading to cortex
Corpus callosum: Major pathway between sides
The brain stem is sometimes referred to as the “trunk” of the brain. It is responsible for many of the neural functions that keep us alive, including regulating our respiration (breathing), heart rate, and digestion.
The cerebellum is critical for coordinated movement and posture.
The two cerebral hemispheres can be further subdivided into four lobes: the occipital, temporal, parietal, and frontal lobes.
-
The occipital lobe is responsible for vision, as is much of the temporal lobe.
-
The temporal lobe is also involved in auditory processing, memory, and multisensory integration (e.g., the convergence of vision and audition).
-
The parietal lobe houses the somatosensory (body sensations) cortex and structures involved in visual attention, as well as multisensory convergence zones.
-
The frontal lobe houses the motor cortex and structures involved in motor planning, language, judgment, and decision-making.
The cerebral hemispheres contain both grey and white matter
-
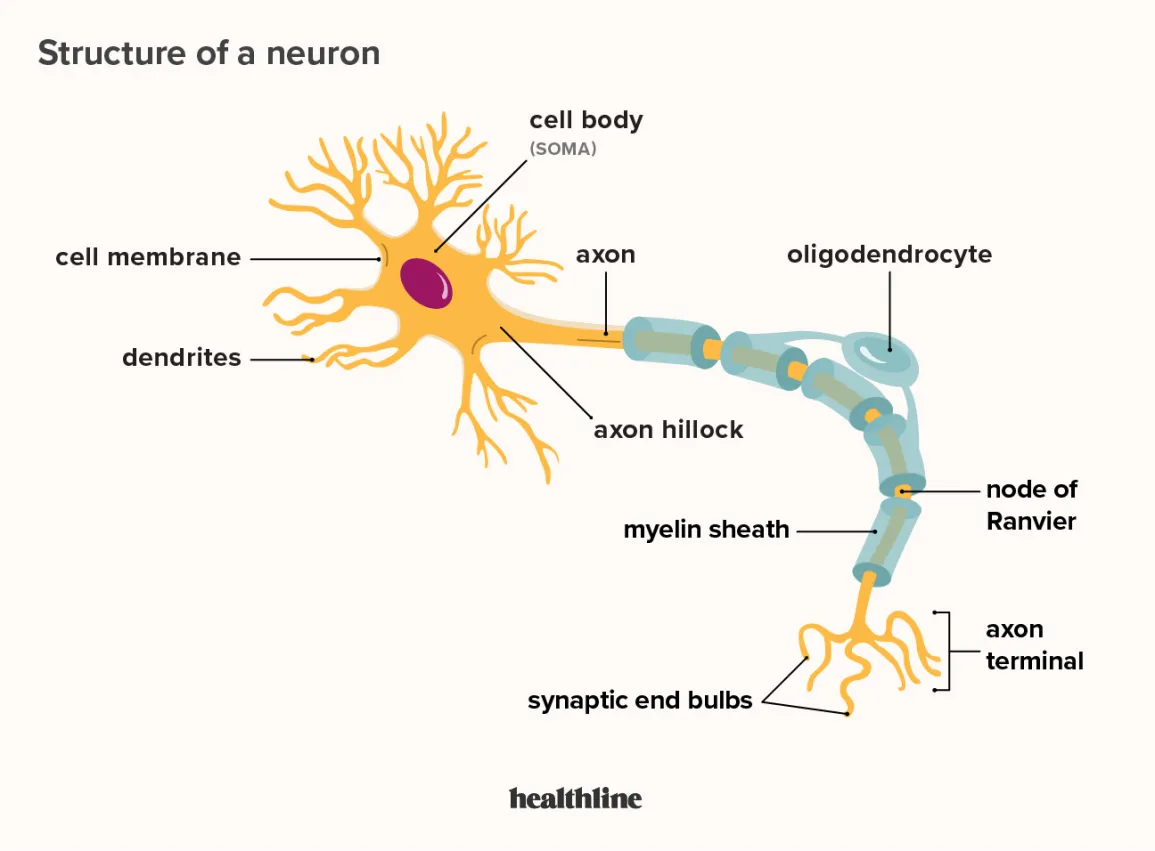
The gray matter is composed of the neuronal cell bodies (see module, “Neurons”). The cell bodies (or soma) contain the genes of the cell and are responsible for metabolism (keeping the cell alive) and synthesizing proteins.
-
The white matter is composed of the axons of the neurons, and, in particular, axons that are covered with a sheath of myelin (fatty support cells that are whitish in color). Axons conduct the electrical signals from the cell and are, therefore, critical to cell communication.